本文最后更新于 2021年5月13日 凌晨
Softmax回归 线性回归(回归):
单连续数值输出
自然区间R
跟真实值的区别作为损失
Softmax回归(分类):
从回归导多类分类 —— 均方损失:
对类别进行一位有效编码(one-hot):
使用均方损失
最大值作为预测:$\hat{y}=argmax \ o_i$
需要更置信的识别正确类(大余量):
指对与正确类的识别远大于非正确类的识别,大于某一阈值(存疑)
将模型的输出作为概率,即输出匹配概率(非负,和为1):
其中某一类型的概率
概率$y$和$\hat y$的区别作为损失
使用exp原因:确保输出为正数且和为1
交叉熵损失 交叉熵用来衡量两个概率(向量)的区别:
可以把$p_i$理解为$y_i \in {0,1}$,q理解为样本属于i类的概率
将它作为损失:
该损失的梯度时真实概率和预测概率的区别:
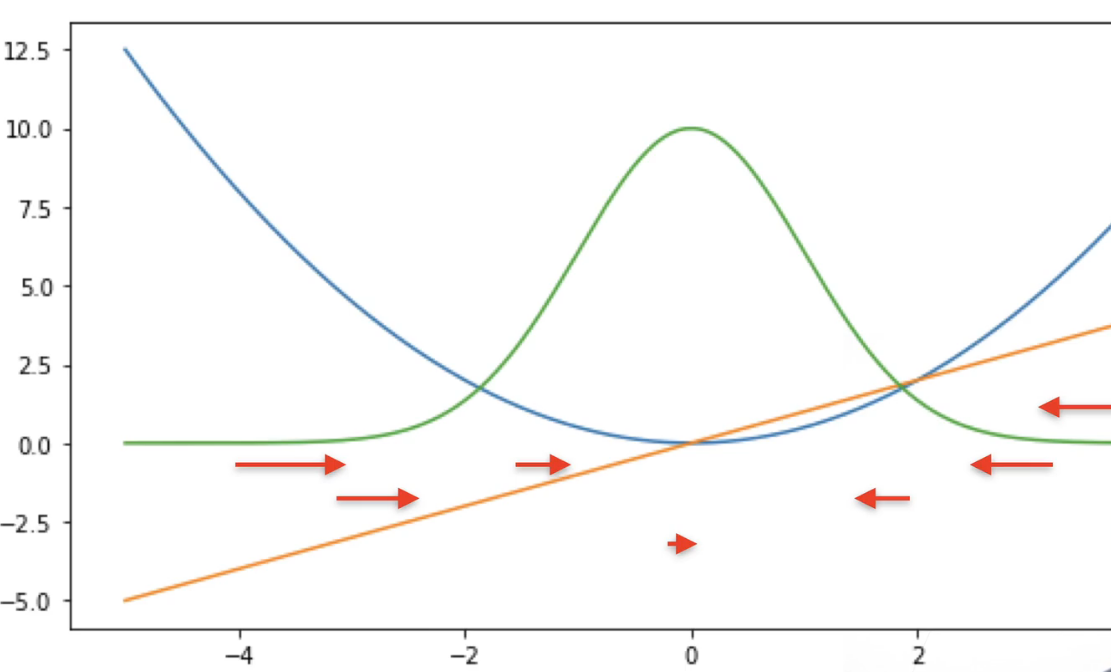
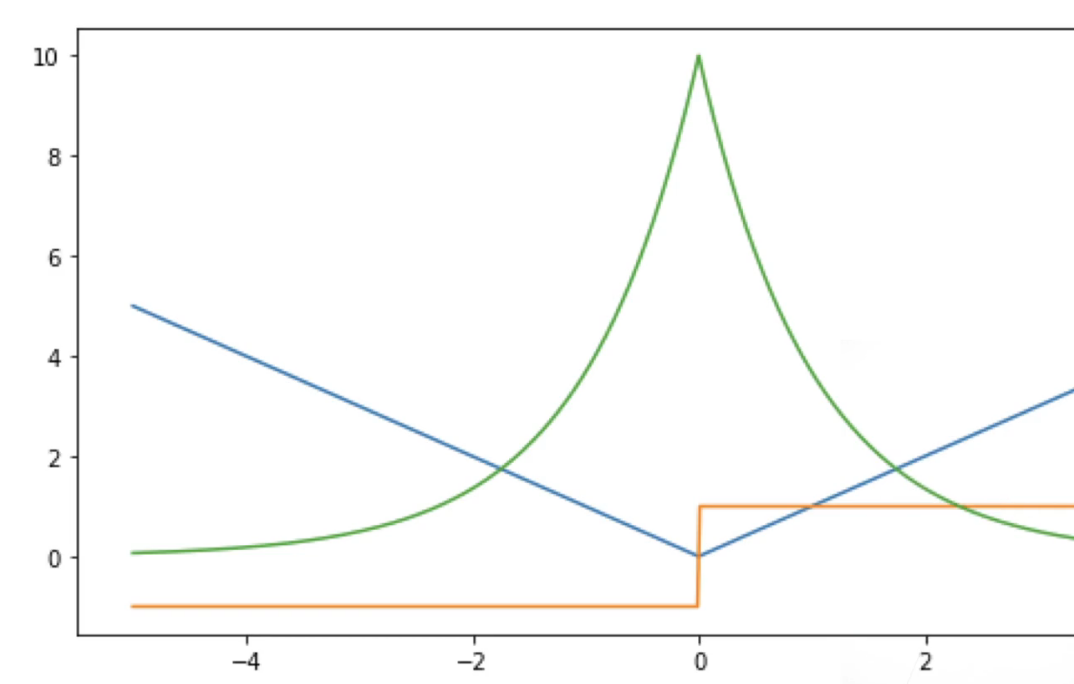
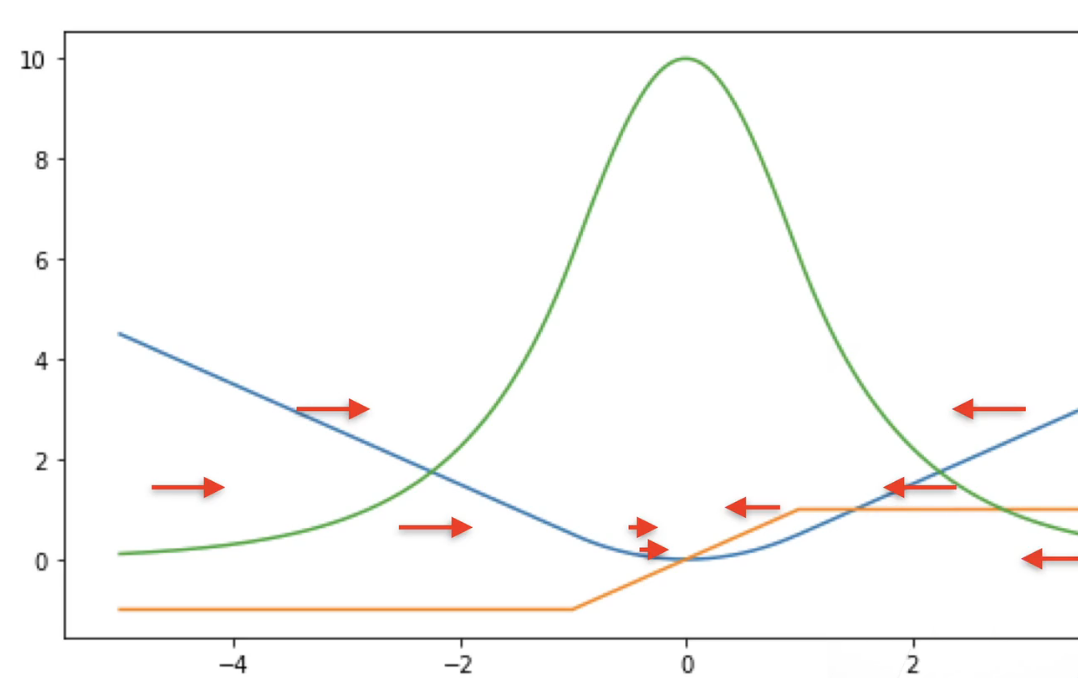
损失函数 L2 Loss
L1 Loss
0点处不可导,0点附近变化大,但是其他地方的梯度为常数稳定
Huber’s Robust Loss 结合L1,L2 Loss
当预测值与真实值偏差大时,梯度为常数,稳定
当偏差较小时,梯度的绝对值越小,越平滑
Softmax回归的从零开始实现 导包,读数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 import torchfrom IPython import displayfrom d2l import torch as d2l256
初始化w,b
1 2 3 4 5 num_inputs = 784 10 0 , 0.01 , size=(num_inputs, num_outputs), requires_grad=True )True )
实现Softmax
1 2 3 4 def softmax (X ):sum (1 , keepdim=True ) return X_exp / partition
实现Softmax回归模型
1 2 3 def net (X ):return softmax(torch.matmul(X.reshape((-1 , W.shape[0 ])), W) + b)
交叉熵损失函数
1 2 3 4 def cross_entropy (y_hat, y ):return -torch.log(y_hat[range (len (y_hat)), y])
计算正确率
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 def accuracy (y_hat, y ): """计算预测正确的数量。""" if len (y_hat.shape) > 1 and y_hat.shape[1 ] > 1 : 1 ) type (y.dtype) == yreturn float (cmp.type (y.dtype).sum ())len (y)
评估任意模型net的准确率
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 def evaluate_accuracy (net, data_iter ): """计算在指定数据集上模型的精度。""" if isinstance (net, torch.nn.Module):eval () 2 ) for X, y in data_iter:return metric[0 ] / metric[1 ]
Accumulator 实例中创建了 2 个变量,用于分别存储正确预测的数量和预测的总数量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Accumulator : """在`n`个变量上累加。""" def __init__ (self, n ):0.0 ] * ndef add (self, *args ):float (b) for a, b in zip (self.data, args)]def reset (self ):0.0 ] * len (self.data)def __getitem__ (self, idx ):return self.data[idx]
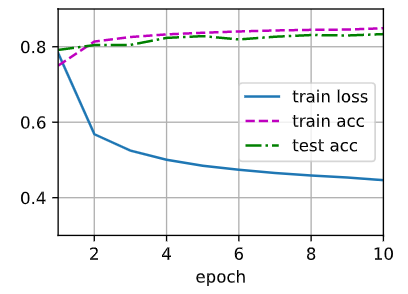
Softmax回归的训练
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 def train_epoch_ch3 (net, train_iter, loss, updater ): """训练模型一个迭代周期(定义见第3章)。""" if isinstance (net, torch.nn.Module): 3 )for X, y in train_iter:if isinstance (updater, torch.optim.Optimizer): float (l) * len (y), accuracy(y_hat, y),else :sum ().backward()0 ]) float (l.sum ()), accuracy(y_hat, y), y.numel())return metric[0 ] / metric[2 ], metric[1 ] / metric[2 ]
训练函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 def train_ch3 (net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, updater ): """训练模型(定义见第3章)。""" 'epoch' , xlim=[1 , num_epochs], ylim=[0.3 , 0.9 ],'train loss' , 'train acc' , 'test acc' ]) for epoch in range (num_epochs):1 , train_metrics + (test_acc,)) assert train_loss < 0.5 , train_lossassert train_acc <= 1 and train_acc > 0.7 , train_accassert test_acc <= 1 and test_acc > 0.7 , test_acc
小批量随机梯度下降来优化模型的损失函数
1 2 3 4 lr = 0.1 def updater (batch_size ):return d2l.sgd([W, b], lr, batch_size)
训练模型10个迭代周期
1 2 num_epochs = 10
对图像进行分类预测
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 def predict_ch3 (net, test_iter, n=6 ): """预测标签(定义见第3章)。""" for X, y in test_iter:break 1 ))'\n' + pred for true, pred in zip (trues, preds)]0 :n].reshape((n, 28 , 28 )), 1 , n, titles=titles[0 :n])
Softmax的简洁实现 初始化网络:
因此,需要定义展平层在线性层前调整输入的形状
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 net = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784 , 10 ))def init_weights (m ):if type (m) == nn.Linear:0.01 )
在交叉熵损失函数中传递未归一化的预测,并同时计算softmax及其对数
1 loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
使用学习率为0.1的小批量随机梯度下降作为优化算法
1 trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.1 )
训练模型
1 2 num_epochs = 10