本文最后更新于 2021年4月29日 上午
线性模型 给定n维输入 $x = [x_1,x_2,…x_n]^T$
线性模型有一个n维权重和一个标量偏差(offset)
输出是输入的加权和
向量版本:$y=\left< w,x \right> +b$
可写成:$y=w^Tx+b$
线性模型可以看作是单层神经网络:输入层$o_1$,输入层为$x_1,x_2,…x_d$
损失函数 比较真实值和预测值的差距,数值越小代表损失越小
设$y$是真实值,$\hat{y}$
平方损失:
其中$\frac{1}{2}$求导时方便约掉,类似SVM模型的优化目标函数
假设有n个样本,记作:
$\mathbf{X}=[\mathbf{x_1},\mathbf{x_2},…\mathbf{x_n}]^T$,$x_i$为向量,$\mathbf{y}=[y_1,y_2,…y_n]^T$,$y_i$为标量
可以得到训练损失:
最小化损失来学习参数:
下面忽略向量粗体,需要注意区分,主要是懒,写起来累
显示解 将偏差加入权重,写起来就可以忽略b:
得到损失函数:
求导(链式法则)得到线性回归的解(解析解):
损失是凸函数,所以最优解满足梯度为0,即:
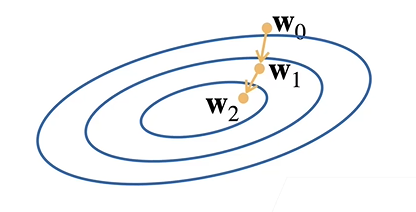
基础优化方法 梯度下降 求不出解析解时可以有效训练模型
选择一个初始值$w_0$
重复迭代参数t=1,2,3
实现过程:沿反梯度方向增加损失函数值(更新参数求解)
$\eta$为学习率:步长的超参数,即沿梯度方向的距离,该参数不能太大也不能太小
小批量随机梯度下降 原因:计算梯度需要遍历整个训练集,慢
只需要随机采样b个样本$i_1,i_2,…,i_b$来计算损失
b为批量大小,超参数,不能太大,也不能太小(不利于并行计算)
线性回归的从零开始实现 不使用框架
我们已知w,b的真实值,然后用真实值加上噪声生成数据集,最后用梯度下降拟合出w和b
导包
1 2 3 4 %matplotlib inlineimport randomimport torchfrom d2l import torch as d2l
生成数据集
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 def synthetic_data (w, b, num_examples ): """ 生成 y = Xw + b + 噪声。 """ 0 , 1 , (num_examples, len (w)))0 , 0.01 , y.shape)return X, y.reshape((-1 , 1 )) 2 , -3.4 ])4.2 1000 )
画图
1 2 3 d2l.set_figsize()1 ].detach().numpy(),1 );
随机抽取样本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 def data_iter (batch_size, features, labels ): len (features)list (range (num_examples))for i in range (0 , num_examples, batch_size):min (i +yield features[batch_indices], labels[batch_indices]10 for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):print (X, '\n' , y)break
定义模型参数
1 2 w = torch.normal(0 , 0.01 , size=(2 , 1 ), requires_grad=True )1 , requires_grad=True )
定义模型
1 2 3 def linreg (X, w, b ): """线性回归模型。""" return torch.matmul(X, w) + b
定义损失函数
1 2 3 def squared_loss (y_hat, y ): """均方损失。""" return (y_hat - y.reshape(y_hat.shape))**2 / 2
定义优化算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 def sgd (params, lr, batch_size ): """小批量随机梯度下降。""" with torch.no_grad():for param in params:
模型训练
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 lr = 0.03 3 for epoch in range (num_epochs):for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels): sum ().backward() with torch.no_grad():print (f'epoch {epoch + 1 } , loss {float (train_l.mean()):f} ' )
估计误差
1 2 print (f'w的估计误差: {true_w - w.reshape(true_w.shape)} ' )print (f'b的估计误差: {true_b - b} ' )
线性回归的简洁实现 准备工作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 import numpy as npimport torchfrom torch.utils import datafrom d2l import torch as d2l2 , -3.4 ])4.2 1000 )
构建一个迭代器来读取样本,有点迷
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 def load_array (data_arrays, batch_size, is_train=True ): """构造一个PyTorch数据迭代器。""" return data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size, shuffle=is_train)10 next (iter (data_iter))
模型建立
1 2 3 from torch import nn2 , 1 ))
全连接层在 Linear 类中定义,其中in_features =2,即对应x,out_features =1对应y
Sequential 类为串联在一起的多个层定义了一个容器,将数据传入到第一层,然后将第一层的输出作为第二层的输入
初始化模型参数
1 2 net[0 ].weight.data.normal_(0 , 0.01 )0 ].bias.data.fill_(0 )
定义损失函数
定义优化算法
1 trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.03 )
模型训练
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 num_epochs = 3 for epoch in range (num_epochs):for X, y in data_iter:print (f'epoch {epoch + 1 } , loss {l:f} ' )